राजर्षी छत्रपती शाहू महाराज जयंतीनिमित्त लेख... *लोककल्याणकारी राजर्षी छत्रपती शाहू महाराज* ---------------------------- -डॉ.श्रीमंत कोकाटे ----------------------------- छत्रपती शाहू महाराजांचा जन्म 26 जून 1874 रोजी कसबा बावडा येथे झाला.1884 साली ते छत्रपतींच्या कोल्हापूर गादीवरती दत्तक म्हणून आले.1884 ते 1894 या दहा वर्षात त्यांनी राजकोट आणि धारवाड या ठिकाणी उच्च शिक्षण पूर्ण केले. 1894 साली त्यांचा राज्याभिषेक झाला. राज्याभिषेकानंतर त्यांनी आपल्या राज्याचा दौरा केला. डोंगरदऱ्यात राहणाऱ्या कष्टकरी, श्रमकरी, शेतकरी, वंचित, उपेक्षित, भूमिहीन प्रजाजनांचे दुःख पाहून त्यांचे मन हेलावले, छत्रपतीच्या अंतःकरणामध्ये प्रचंड वात्सल्य होते. ते जसे स्वाभिमानी होते, तसेच ते प्रेमळ होते. आपल्या राज्यात अमुलाग्र बदल करण्याचा संकल्प त्यांनी केला. राज्यारोहणामुळे शाहू महाराजांचा सत्कार पुण्यातील सार्वजनिक सभेने आयोजित केला होता, त्यादरम्यानच पुण्यात हिंदू-मुस्लिम दंगल झालेली होती आणि या दंगलीला टिळकाची मदत होती, टिळक हे वयाने शाहू महाराजांपेक्षा वीस वर्षांनी मोठे होते. सत्कार प्रसंगी शाहू महाराज म्
Posts
Showing posts from June, 2023
Rajshri Chhatrapati Shahu Maharaj : A Social Reformer
- Get link
- Other Apps
Chhatrapati Shahu Maharaj, also known as Rajarshi Shahu, was a prominent king in Maharashtra during the 17th and 18th centuries. He was the grandson of the great Maratha king, Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj, and played an important role in the establishment and development of the Maratha Empire. Shahu Maharaj was born in 1682 in Purandar Fort near Pune, Maharashtra. He was the son of Sambhaji Maharaj, who was the eldest son of Chhatrapati Shivaji, but was captured and killed by the Mughal emperor Aurangzeb. After his father's death, Shahu Maharaj was captured by the Mughal emperor and held as a prisoner for several years. He was eventually released by the Mughal emperor Bahadur Shah and returned to Maharashtra in 1707. Upon his return, Shahu Maharaj took up the cause of the Maratha Empire and worked tirelessly to establish and expand its power. He established schools in Nanded, Satara, and Mahabaleshwar to promote education among the people. He also implemented progressive and modern
Sentence and Types of Sentences
- Get link
- Other Apps
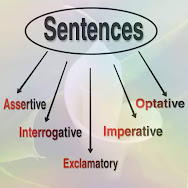
Sentence Introduction: A sentence is a grammatically complete unit of language that expresses a complete thought. It is typically composed of one or more words that are arranged in a specific order according to the rules of grammar and syntax. A sentence can be made up of a subject, a verb, and an object, or it can be a simple statement that doesn't include all three components. The subject of a sentence is usually a noun or pronoun that performs the action of the verb, or about which something is being said. The verb is a word that expresses an action or state of being, and it usually follows the subject. The object is the noun or pronoun that receives the action of the verb. Sentences can be classified based on their structure. A simple sentence consists of one independent clause, which contains a subject and a verb and expresses a complete thought. A compound sentence contains two or more independent clauses joined by a coordinating conjunction such as "and," "or,
Tenses and Types of Tenses
- Get link
- Other Apps
Tenses are a crucial aspect of English grammar, and they play a significant role in communication. They are used to indicate the time at which an action takes place, whether it is in the past, present, or future. There are three main types of tenses: 1. Present Tense 2. Past Tense 3. Future Tense Each of these types of tenses can be further divided into four different forms, depending on the nature of the action: 1. Simple Tense 2. Continuous Tense 3. Perfect Tense 4. Perfect Continuous Tense Let's take a closer look at each of these types of tenses in detail: 1. Present Tense: This tense is used to describe actions that are happening now or are ongoing. It can be further divided into four forms: a. Simple Present Tense: This tense is used to describe habitual actions or general truths. For example, "The sun rises in the east." b. Present Continuous Tense: This tense is used to describe actions that are happening now or in the near future. For example, "I am studyin
Tenses and Types of Tenses
- Get link
- Other Apps
Tenses are a crucial aspect of English grammar, and they play a significant role in communication. They are used to indicate the time at which an action takes place, whether it is in the past, present, or future. There are three main types of tenses: 1. Present Tense 2. Past Tense 3. Future Tense Each of these types of tenses can be further divided into four different forms, depending on the nature of the action: 1. Simple Tense 2. Continuous Tense 3. Perfect Tense 4. Perfect Continuous Tense Let's take a closer look at each of these types of tenses in detail: 1. Present Tense: This tense is used to describe actions that are happening now or are ongoing. It can be further divided into four forms: a. Simple Present Tense: This tense is used to describe habitual actions or general truths. For example, "The sun rises in the east." b. Present Continuous Tense: This tense is used to describe actions that are happening now or in the near future. For example, "I am studyin
Introduction to Linguistics
- Get link
- Other Apps
Linguistics Linguistics is the scientific study of language and its structure, including the sounds, words, grammar, semantics, and social contexts of language use. It is concerned with understanding how language is acquired, how it is used, how it changes over time, and how it varies across different cultures and communities. The study of linguistics can be divided into several subfields, including phonetics, phonology, morphology, syntax, semantics, pragmatics, and sociolinguistics. Phonetics is concerned with the physical properties of speech sounds, including their production, transmission, and perception. It focuses on the articulation of sounds, the acoustic properties of speech, and the ways in which sounds are perceived by listeners. Phonology is concerned with the abstract patterns of sounds in language, including the ways in which sounds are organized and combined to form words. It examines the rules for combining sounds to form syllables and words, and the ways in which